Introduction to Photorealism Art
Photorealism, also known as hyperrealism, is an art movement that began in the late 1960s, characterized by the meticulous reproduction of photographic images through painting, drawing, and other media. The goal of photorealism is to create artworks that are indistinguishable from high-resolution photographs, capturing intricate details and textures with extraordinary precision. This art form challenges traditional approaches to representation by emphasizing the technical skill required to mimic the photographic quality.
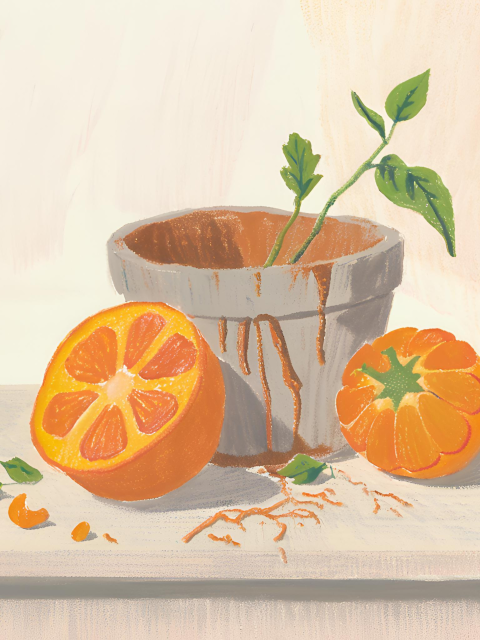
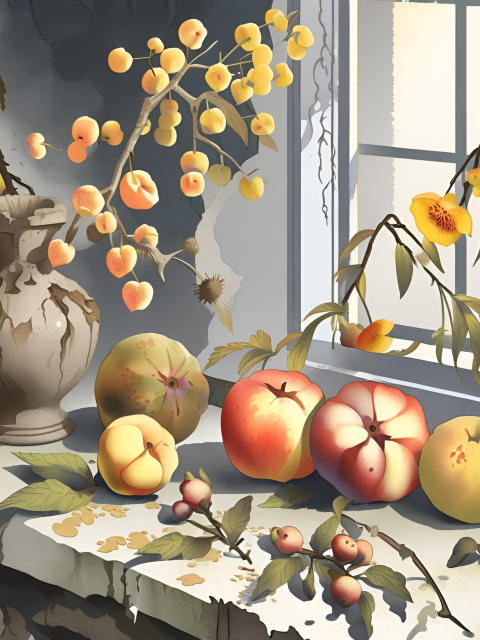
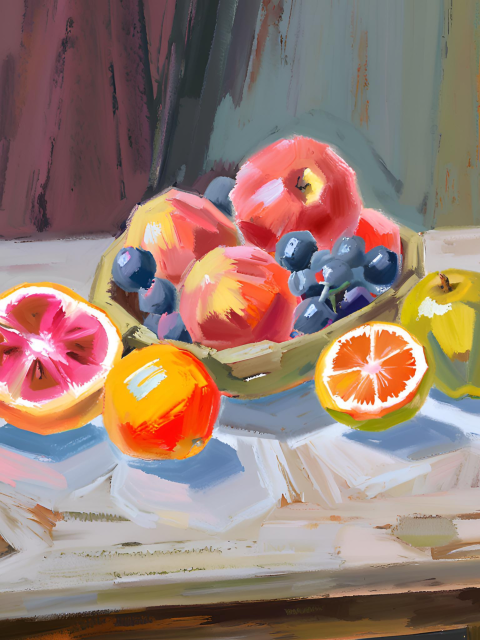





Characteristics of Photorealism Art
- High Detail: Photorealistic artworks are known for their extreme attention to detail, replicating textures, lighting, and reflections as seen in photographs.
- Precision: Artists employ precise techniques to ensure that every aspect of the subject is rendered with accuracy, creating a lifelike appearance.
- Use of Photographs: Photorealist artists often use photographs as reference material, and may project or trace these images to ensure accuracy in their work.
- Realism: The aim is to create an illusion of reality, presenting scenes and subjects as they appear in everyday life with a high level of fidelity.
- Technical Mastery: Requires exceptional technical skill and patience, as artists work meticulously to achieve the fine details that characterize the style.
Mediums and Techniques
- Oil Painting: Commonly used for its ability to create smooth textures and rich colors, allowing for meticulous blending and detailing.
- Acrylic Painting: Provides a faster-drying alternative to oil paints, suitable for achieving precise details and layering effects.
- Graphite Drawing: Utilizes pencils for creating highly detailed drawings, capturing the subtle nuances of light and shadow.
- Airbrush: Employed for its ability to produce smooth gradients and precise details, often used in conjunction with other painting methods.
- Digital Tools: Some contemporary photorealist artists use digital techniques to assist in planning and rendering, including image manipulation software.
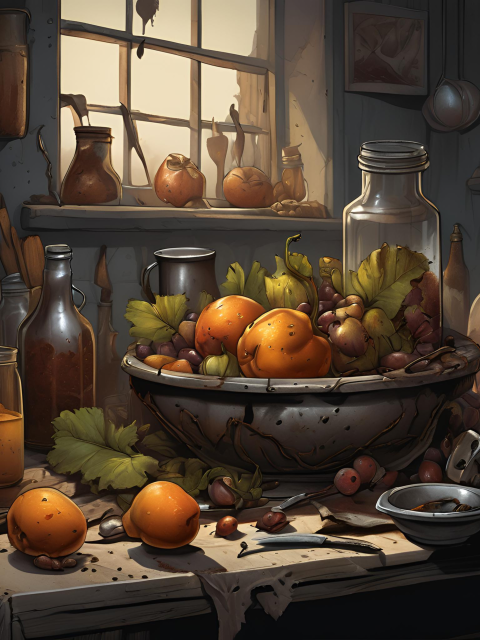
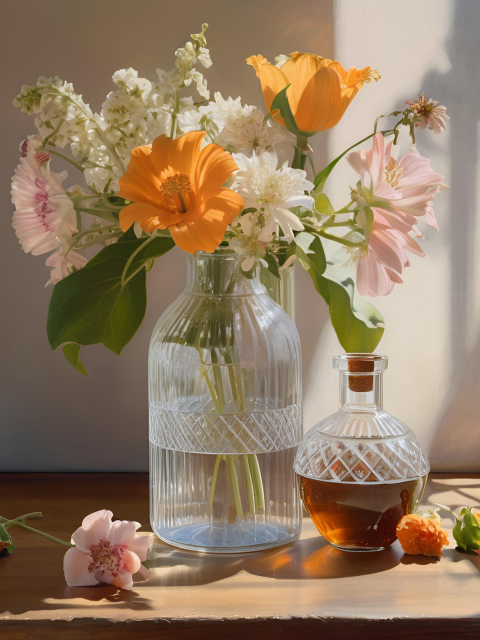
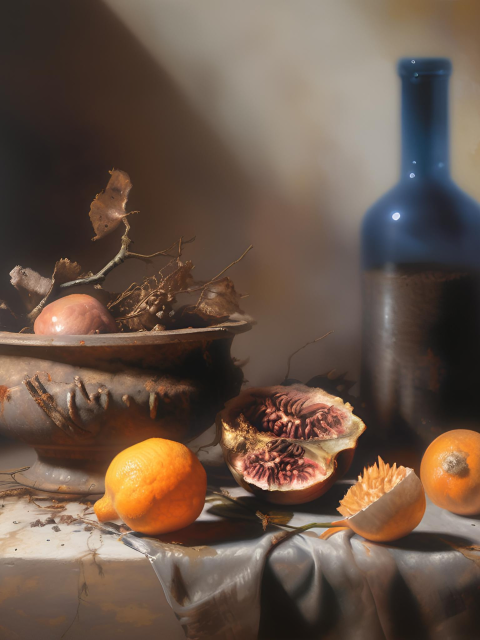
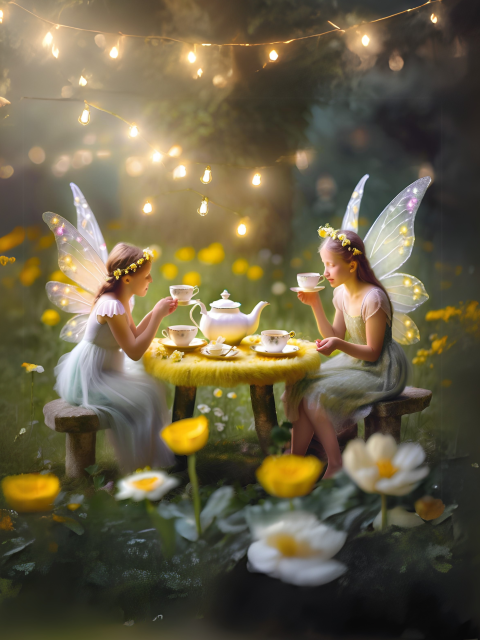
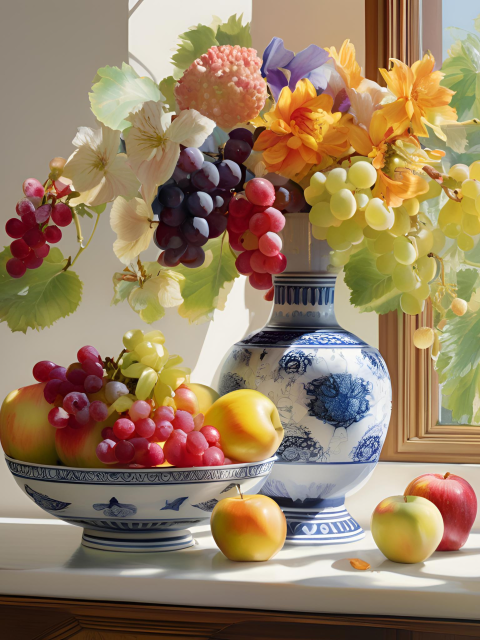
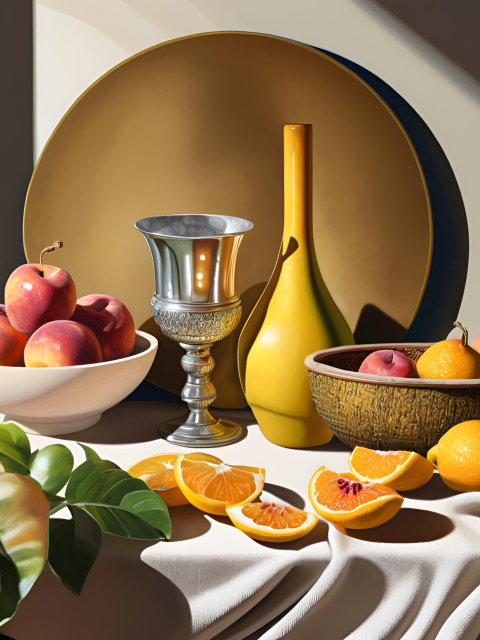






Artistic Expression
- Realistic Representation: Focuses on creating highly accurate depictions of subjects, blurring the line between painting and photography.
- Exploration of Perception: Challenges viewers’ perceptions of reality and art by presenting scenes that are so lifelike they mimic photographic images.
- Attention to Detail: Highlights the artist’s dedication to capturing minute details, reflecting the complexity and richness of everyday life.
- Commentary on Photography: Explores the relationship between painting and photography, often questioning the nature of representation and the role of technology in art.
Functionality
- Visual Impact: Aims to achieve a striking visual effect by creating artworks that closely resemble high-resolution photographs, often leading to a sense of realism and immediacy.
- Technical Demonstration: Showcases the artist’s technical skills and mastery of their medium, emphasizing the precision and patience required for photorealistic work.
- Exploration of Realism: Provides a platform for exploring and reinterpreting the concept of realism in art, challenging traditional boundaries and perspectives.
- Cultural Reflection: Often reflects contemporary life and urban environments, providing detailed insights into modern society and its visual culture.
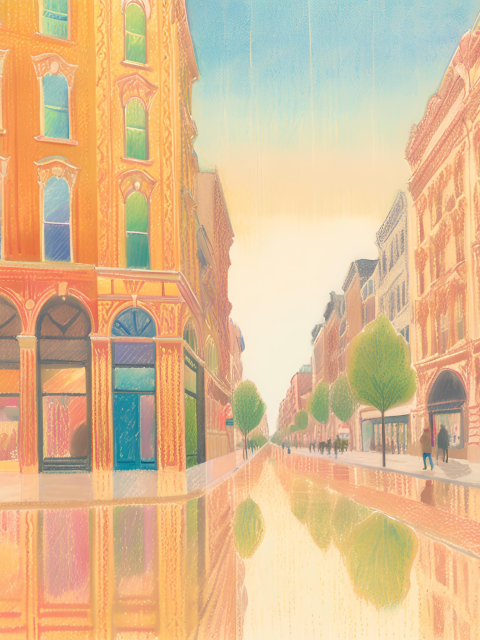
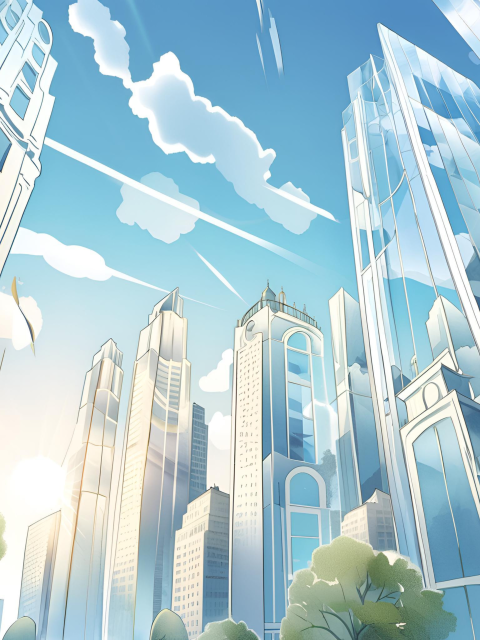
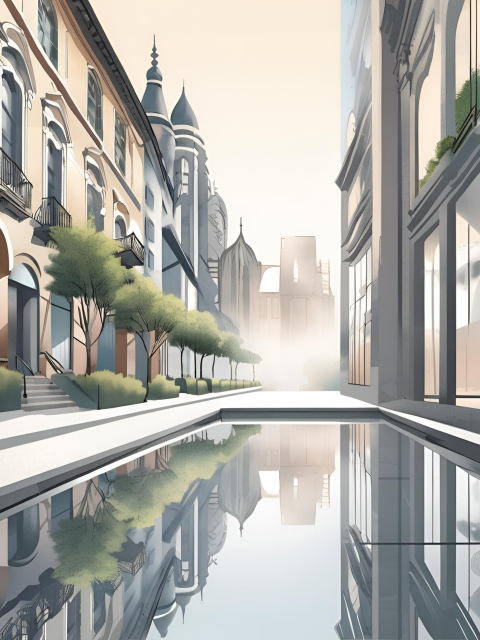






Locations
- Art Galleries and Museums: Photorealistic works are frequently exhibited in galleries and museums, showcasing the precision and detail of the art form to a broad audience.
- Public Installations: Some photorealist artworks are displayed in public spaces, including murals or large-scale installations, making them accessible to a wider audience.
- Art Fairs and Exhibitions: Presented at art fairs and exhibitions, where photorealism is highlighted alongside other contemporary and realistic art forms.
- Online Platforms: Increasingly shared on digital platforms, allowing artists to reach a global audience and showcase their detailed work.
Themes of Photorealism
- Everyday Life: Focuses on ordinary and mundane subjects, capturing the beauty and complexity of daily life with precise detail.
- Urban Environments: Depicts cityscapes and urban scenes, emphasizing the reflective surfaces and intricate details of modern architecture and environments.
- Nature and Objects: Represents natural scenes and objects with a high level of realism, often highlighting the textures and subtleties of the physical world.
- Perception and Reality: Investigates the nature of reality and representation, questioning the boundaries between photography and painting.


Key Examples
- Chuck Close (Portraiture): Known for his large-scale, hyper-detailed portraits that explore the nuances of facial features and textures.
- Audrey Flack (Still Life and Portraits): Creates meticulously detailed paintings of everyday objects and portraits, capturing their vibrancy and texture.
- Ralph Goings (Urban Scenes): Focuses on the American consumer culture and urban life, depicting ordinary scenes with precise photorealistic techniques.
- Richard Estes (Cityscapes): A pioneer of photorealism, known for his reflective urban scenes and detailed depictions of city environments.
- Robert Bechtle (Suburban Scenes): Captures the tranquility and detail of suburban life, showcasing everyday scenes with photorealistic precision.
Description
Photorealism is an art style dedicated to creating artworks that are highly accurate and detailed, resembling high-resolution photographs. It emphasizes the technical skill required to replicate the minutiae of the subject matter, focusing on everyday scenes, urban environments, and portraits. By blurring the line between photography and painting, photorealism challenges traditional artistic boundaries and explores the nature of realism and representation.
Historical Context
Emerging in the late 1960s, photorealism was a response to the abstract and conceptual art movements of the time. It sought to return to traditional methods of representation, exploring the relationship between photography and painting. The movement was influenced by advancements in photographic technology and a growing interest in visual accuracy.
Construction Techniques
- Photo Projection: Using projectors to trace or project photographic images onto canvases, ensuring precise replication of details.
- Layered Brushwork: Applying layers of paint or graphite to achieve detailed textures and smooth transitions.
- Digital Assistance: Utilizing digital tools for planning and rendering, including image manipulation software to enhance accuracy and detail.
- Fine Detailing: Employing fine brushes and meticulous techniques to capture the minute details of the subject matter.
5 Simple Prompts for AI-Generated Art
- “Create a photorealistic painting of a still life scene with detailed textures and precise lighting.”
- “Design a photorealistic urban landscape that emphasizes reflections and architectural details in a cityscape.”
- “Generate a highly detailed portrait that replicates the precision and realism of a high-resolution photograph.”
- “Imagine a photorealistic depiction of a domestic scene, focusing on the accurate representation of objects and light.”
- “Visualize a photorealistic artwork that captures the complexities of modern life and urban environments with meticulous detail.”
Conclusion
Photorealism is a distinctive art style characterized by its commitment to achieving photographic accuracy and detail. By focusing on everyday subjects, urban landscapes, and portraits, photorealism challenges traditional artistic boundaries and explores the nature of realism and representation. Its emphasis on technical skill and precision provides a unique perspective on contemporary life and the role of technology in art.